
Consumer Cognition With Respect To E-Commerce During Pandemic
Abhishek Kaushal[1]
ABSTRACT
The Corona virus outbreak has impacted the global economy and has affected the lives of millions of people. As social distancing is the need of an hour, we can see changes in consumer’s shopping behaviour. During the pandemic, consumers shifted from offline mode to online mode because getting essentials without contact was the preferred way of shopping in the initial stage of this pandemic. E-Commerce became the chosen method to shop every little thing as it was easy, accessible and hassle free. This study attempts to explain how E-Commerce changed consumer behaviour during Pandemic.
KEYWORDS:
Consumer, Cognition, e-Commerce, Coronavirus, Pandemic
INTRODUCTION
A consumer is a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Consumerintends to order, orders, or uses purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities.
Cognition is a term referring to the mental processes involved in gaining knowledge and comprehension. These cognitive processes include thinking, knowing, remembering, judging, and problem-solving.These are higher-level functions of the brain and encompass language, imagination, perception, and planning.
Types of Cognitive Processes
- Attention: Attention is a cognitive process that allows people to focus on a specific stimulus in the environment.
- Perception: Perception is a cognitive process that allows people to take in information through their senses (sensation) and then utilize this information to respond and interact with the world.
- Learning: requires cognitive processes involved in taking in new things, synthesizing information, and integrating it with prior knowledge.
- Memory: Memory is an important cognitive process that allows people to encode, store, and retrieve information. It is a critical component in the learning process and allows people to retain knowledge about the world and their personal histories.
- Thought: Thought is an essential part of every cognitive process. It allows people to engage in decision-making, problem-solving, and higher reasoning.
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services, or the transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic network, primarily the internet. It is the buying and selling of products through an electronic medium- like the internet. These business transactions occur either as business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), consumer-to-consumer or consumer-to-business.
TYPES OF E-COMMERCE
There are three main types of e-commerce: business-to-business (websites like Shopify), business-to-consumer (websites such as Flipkart, Amazon), and consumer-to-consumer (websites like eBay, Meesho).
i) Business-to-Business: Business-to-business, or b2b, is the practice of selling online from one business to another, in other words, wholesale.
ii) Business-to-Consumer: or is b2c, is for businesses to target specific consumers online. Businesses are able to put their products online, allowing the consumer to purchase the products in the comfort of their own home, saving them some precious time.
iii) Consumer-to-Consumer: a rejected consumer good may be sold through it. Like an unwanted shirt at the back of wardrobe, never worn. The consumers are able to upload images of the product and sell it on to others that may be interested in buying it.
ADVANTAGES OF USING E-COMMERCE
- Ease to access: Selling on the web is quick and simple. Many consumers disregard buying products if they know they need to travel to the store to purchase it.
- Variety and range of Products: a vast array of products can be stored on internet. There is no limit to what can be stored on the internet. Anything from edibles to pillows and mobile phones can be bought online. As well as this, there is no limit as to how the products are bought. Many companies are turning to social media channels, such as Facebook and Instagram, to target specific customers and push certain products.
- Availability round the clock: The beauty of the internet is that, by providing access to any internet connection, it’s available at all time of the day or night.
- All Over the World: One of the many wonderful things about the World Wide Web is that it is truly world-wide. Whether consumers are in Canada, Zambia or the UK, they have got access to a plethora of websites to help satisfy online needs.
- Man vs. Machine: Computers are able to store masses of information, available to almost anyone at the touch of a button; we, as humans, are prone to forgetting bits of information. Therefore, having an online presence help provide customer with all the information they need to know more about any business. Nowadays, the majority of customers to do their research, so what better way to provide all the information they need.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. Some become seriously ill and require medical attention. Older people and those with underlying medical conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, or cancer were more likely to develop serious illness. Anyone can get sick with COVID-19 and become seriously ill or die at any age. It has been declared as pandemic by WHO in 2020.
Pandemic is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic disease with a stable number of infected individuals is not a pandemic. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide. Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The most fatal pandemic in recorded history was the Black Death/Plague, which killed an estimated 75–200 million people in the 14th century (Reuters, 2008; Wired, 2001; DeLeo et al, 2005). The term was not used yet but was for later pandemics including the 1918 influenza pandemic (Spanish flu) (CDCP, 2020; Rosenwald, 2020 WHO, 2010). Merriam-Webster defines pandemic as occurring over a wide geographic area and affecting an exceptionally high proportion of the population. It further reports that, pandemic is the seventh most frequently looked-up word in its online dictionary this year.
When the corona virus cases were found in India, it went on complete lockdown, only essential goods and services were available. It resulted in a boom in the e-commerce of FMCG goods. When the lockdown was announced in India, people went on to buying essentials like sanitizers, eatables etc. to stock up and this way people started searching for such goods online because of the limited availability offline. Of course, the main reason for people to shift from offline to online was to avoid contact with the people. People were working from home and are now still continuing the same. This made people consume a lot more because restaurants, hotels were shut. So, online was and is the safest option left even though we are now coming back to normal slowly.
Keeping in view, the same, present study is framed as, “Consumer Cognition with respect to E-Commerce during Pandemic”. The researcher wants to review that how consumers attend to and perceive consumption with respect to e-commerce during pandemic.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Writankar Mukherjee, Sagar Malviya (May4, 2020) Top multinational from HUL
India’s largest FMCG goods company HUL chairman Sanjiv Mehta said customers have this fear of coronavirus due to which they are scared of going out to buy even essential goods for them. Online FMCG sales rose to 50% YOY during the March quarter as consumers are more interested in shopping e-grocers instead of local kiranas. In Nielsen report, they mentioned that local retailer share fell by 220 bps, entirely taken by either ecommerce or modern retailers in this pandemic lockdown.
Nath.S. (April 28, 2020) Did the lockdown accelerate the digitization of India Inc?
Sanstuti Nath threw light on the term ‘digital consumption’. Her study on the consumption patterns of consumers’ post-pandemic lockdown showed that the e-commerce companies have seen a significant growth of 70-100% for essential commodities. And this sudden adoption of digital platforms can be allocated to mobile advertising. Top companies and brands were already benefiting themselves from these platforms, and also now post lockdown this whole scenario is going to change how consumers buy.
Avatar.P (May 05, 2020) lockdown 3.0: Flipkart, Snapdeal sees heavy traffic for non -essential items.
As with the ongoing lockdown period, FMCG products are on high demand, but once the lockdown gets over, how consumer behaviour is going to change is a big question. With the lockdown 3.0, e-commerce platforms have been permitted to sell non Essential items in the orange and green zones and with this Flipkart have stated that the most searched belongs to the personal care products like trimmers, electronic goods like mobiles, laptops, and fans air conditioners to beat the heat. Snapdeal claimed that they have received a huge proportion of 75% of the total orders from these orange and green zones in the country. Estimates are that there would be huge demands for items like these post lockdown period.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
- To map out buying behaviour of Consumers during pandemic.
- To study Consumer Cognition with respect to e-Commerce during pandemic.
METHODOLOGY
Research design: the study adopted a Descriptive Survey research design. Non-participant observation was also followed.
Sampling stratification
A total of 66 participants were approached for data collection. However, the researcher received back only 52 valid responses.
| Universe | Sample Size (N) | Type |
| Bhopal (MP) | 52 | Purposive |
ASSESSMENT MEASURE
The assessment measure taken for the study is a self-developed and standardized questionnaire. It comprises of nine questions divided into various scales. It was administered on various respondents. Respondents were given the liberty to take their time for answering. The confidentiality of their responses was assured. Non-participant observation was also made. The results were drawn by coding the responses answered through the tool.
PROCEDURE
The respondents were approached according to their convenience. A good rapport was established with them. Then, the questionnaire was administered on them. Respondents were given the liberty to take their time for answering. The confidentiality of their responses was assured. Non-participant observation was also made. In the end, the participants were thanked for their cooperation.
RESULT AND ANALYSIS
N=52
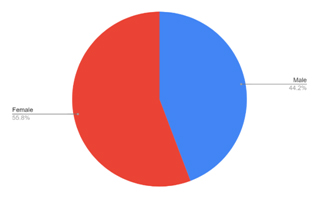
Table 1: Showing gender of Respondents
| SN | Gender | Percentage |
| 1 | Male | 44.2 |
| 2 | Female | 55.8 |
 |
||
Females surpassed males in e-shopping. The reason that the majority of consumers are female is, females mostly engage in the essential and household shopping.
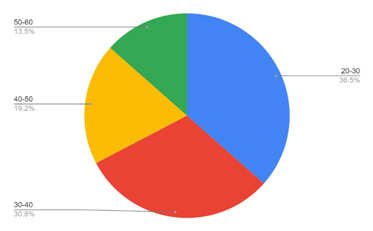
Table 2: Showing age group of Respondents-
| SN | Age Group | Percentage |
| 1 | 50-60 | 13.5 |
| 2 | 40-50 | 19.2 |
| 3 | 30-40 | 30.8 |
| 4 | 20-30 | 36.5 |
 |
||
The majority of the consumers who shifted from offline to E-Commerce are aged between 20-30 years, reason being awareness. Along with this not to forget that older people still believe in traditional shopping.
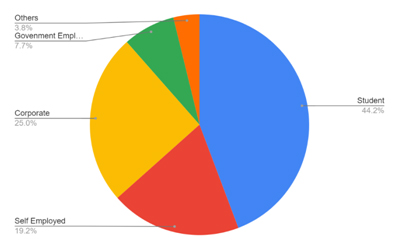
Table 3: Showing occupation of Respondents-
| SN | Occupation | Percentage |
| 1 | Government employees | 7.7 |
| 2 | Corporate | 25 |
| 3 | Self-employed | 19.2 |
| 4 | Student | 44.2 |
| 5 | Others | 3.8 |
 |
||
Mostly students and the corporate workers participated in this survey. These are the people who either work from home or study from home.
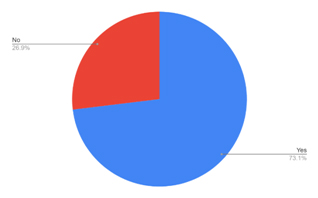
Table 4: Showing purchase of essential goods through e-commerce before the Pandemic
| SN | Response | Percentage |
| 1 | Yes | 73.1 |
| 2 | No | 26.9 |
 |
||
This shows the consumers who bought essentials online before the Pandemic. We can see there were a lot of people who used to buy the essential stuff online. The reason can be the people who work in the corporate sector buy such stuff online.
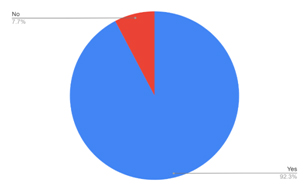
Table 5: Showing purchase of goods through e-commerce during Pandemic
| SN | Response | Percentage |
| 1 | Yes | 92.3 |
| 2 | No | 7.7 |
 |
||
Here we can see the purchase of goods through e-commerce during Pandemic. Hardly any were left to use e-commerce (7.7%).
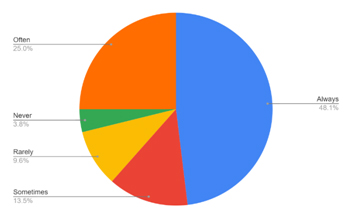
Table 6: Showing purchase of goods through e-commerce post-Pandemic
| SN | Responses | Percentage |
| 1 | Always | 48.1 |
| 2 | Often | 25 |
| 3 | Sometimes | 13.5 |
| 4 | Rarely | 9.6 |
| 5 | Never | 3.8 |
 |
||
The result clearly indicates that, most of the consumers prefer to purchase goods through e-commerce post-Pandemic.
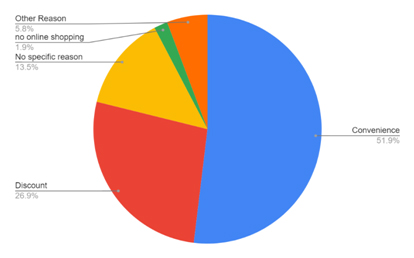
Table 7: Showing reason behind purchase of goods through e-commerce
| SN | Reason behind purchase of goods | Percentage |
| 1 | Discount | 26.9 |
| 2 | Convenience | 51.9 |
| 3 | No online shopping | 1.9 |
| 4 | No specific reason | 13.5 |
| 5 | Other reason | 5.8 |
 |
||
More than half of the respondents buy goods through e-commerce because it is convenient and other people buy because of great discounts available online. Other reasons mentioned were, they feel safe, and they are still scared to go out.
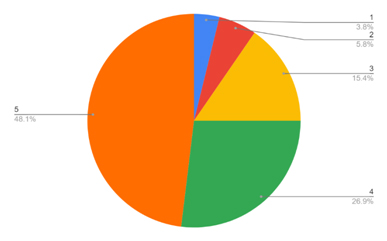
Table 8: Showing satisfaction with e-commerce on the scale of 1-5
(1 being highly dissatisfied and 5 being highly satisfied)
| SN | Scale | Percentage |
| 1 | 5 | 48.1 |
| 2 | 4 | 26.9 |
| 3 | 3 | 15.4 |
| 4 | 2 | 5.8 |
| 5 | 1 | 3.8 |
 |
||
Respondents are very much satisfied with e-commerce (48% preferred rank 1).
Table 9: Showing preference of e-commerce over conventional shopping
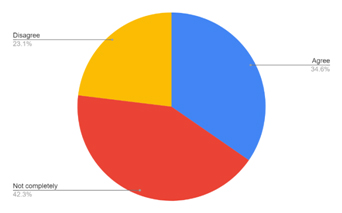
| SN | Preference | Percentage |
| 1 | Agree | 34.6 |
| 2 | Not completely | 42.3 |
| 3 | Disagree | 23.1 |
 |
||
This shows how customers are happy with online shopping while there are consumers who still don’t want to completely rely on online shopping.
FINDINGS OF STUDY
These results show how different respondents reacted towards the survey and there are different sets of questions to know the consumer behavior cognition towards the e-commerce during the Pandemic.
- Majority of the respondents used to buy the essential stuff online, pre-pandemic.
- E-commerce had a hike during pandemic (result-5).
- Most of the consumers prefer to purchase goods through e-commerce post-Pandemic too.
- More than half of the respondents buy goods through e-commerce because it is convenient and other people buy because of great discounts available online. Other reasons mentioned were, they feel safe, and they are still scared to go out.
- Respondents are very much satisfied with e-commerce (48% preferred rank 1).
- Consumers are happy with online shopping while there are consumers who still don’t want to completely rely on online shopping.
CONCLUSION:
The research shows that pandemic impacted a lot on consumer’s shopping patterns and COVID-19 helped E-commerce to generate more customers because everyone was home quarantined and people were scared to step out from their house, so the preferred method to buy goods was online. E-commerce industry got a lot of new customers. And people are willing to buy things online post the strict lockdown. Though the lockdown has eased, some people are still scared to go out and moreover, it’s easy to buy stuff online. According to the consumers, E-Commerce played a vital role during the lockdown. The survey Results are supportive that more than 50% of customers have changed their traditional shopping habits by ordering products online. This is there as, consumers attended to and perceived e-commerce consumption during pandemic. Though the behaviour changes are not permanent, we can already see consumer’s inclination towards digital adoption. Thus, Cognition with respect to E-Commerce during pandemic is clear.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- ABC/Reuters. Black Death discriminated between victims (ABC News in Science). Australian Broadcasting Corporation (29th of January 2008). Archivedfrom the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 3rd February, 2022.
- Black Death’s Gene Code Cracked. Wired. 3rd October 2001. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 3rd February, 2022.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCS). 1918 Pandemics (H1N1 virus). Retrieved 3rd February, 2022.
- DeLeo, F.R.; and Hinnebusch, B.J. (September 2005). A plague upon the phagocytes. Nature, Medicine, Vol.11 (9) 927–928. doi:10.1038/nm0905-927. PMID 16145573. S2CID 31060258.
- Dou, Y. (2017). Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak. World Health Organization, World Health Organization, www.who.int/westernpacific/emergencies/covid-19. Coronavirus Resources for Retailers. NRF, nrf.com/resources/retail-safety-and-security-tools/coronavirus-resources-retailers.
- Halan, D. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on Online Shopping in India. retail.economictimes.indiatimes.com/retales/impact-of-covid-19-on-online-shopping-in-india/4115.
- Mukherjee, W.; and Malviya, S. (2020). Top multinational from HUL to Apple brace for rising online sales post Covid-19 (4th May, 2020). https://hrnxt.com/news/investment/bengalurubased-startup-wagonfly-secures-500k-investment-from-iti-growth/18307/2020/04/29/
- Reddy, A. (2020). Covid-19 Impact: Consumers Move More towards Digital. www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/covid-19-impact-consumers-move-more-towardsdigital/article31337127.ece.
- Rosenwald, M.S. (2020). History’s deadliest pandemics, from ancient Rome to modern America. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 7 April 2020. Retrieved 3rd February, 2022.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Weekly Virological Update on 05th August 2010. Archived from the original on 7 August 2015. Retrieved 3rd February, 2022.
Nath, S. (2020).Did the lockdown accelerate the digitisation of India Inc? (April 28, 2020). Retrieved 3rd February, 2022. https://www.exchange4media.com/marketing-news/did-the-lockdown-accelerate-the-digitisation-of-india-inc-104236.htmlAnnexure
[1]Assistant Professor, SAGE University, Bhopal
abhishekmkaushal@gmail.com
